Can you identify if your device is infected with malware?
Diagnosing a computer for malware is pretty straightforward. For instance, your machine will slow down, the fan makes whirring noise all the time, unknown icons keep appearing on the desktop, heating issues crashes, and much more.
These factors are more than enough to conclude that your computer is infected with malware.
However, it is equally challenging to know if your smartphone is compromised. The increasing rate of cyberattacks is a significant concern, and it is vital to understand how the malware reaches your phone. It will help you be safe from them.
Therefore, I created this guide to help you understand how hackers infect Android smartphones with malware programs. Further, we will see the methods to remove these malware programs from your device.
So, without any further ado, let’s begin.
Table of Contents
How Hackers are Infecting Phones with Malware
Cybercriminals usually target weak security devices to commit their crimes. It helps them gain more profit using fewer efforts since people with no knowledge about the malware infections are generally those who end up being vulnerable.
There are multiple ways a cybercriminal can access your device or victimize you for personal agendas. Let’s look at some heavily used methods.
1. Infected Applications
The most common form of spreading malware on users’ phones is via using a genuine-looking application.
Cybercriminals often tear down a paid application, insert their malicious code, and create a new package out of it. Later, they upload this infected package on third-party app stores or other websites. Innocent users trying to get the paid app for free download the tweaked version. Thus, installing the malware on their phone unknowingly.
Sometimes, hackers also come up with a brand new application to infect user devices. Such applications are available on third-party app stores. These websites keep their security check lower than standard ones like Google’s Play Store or Apple’s AppStore. Therefore, it is much easier to upload rogue software on such platforms.
However, it is with mentioning that even Google’s and Apple’s official app stores have seen various malicious apps in their collection. They do a regular check to remove such programs. Still, it happens after thousands or sometimes millions of downloads.
There have been multiple instances where big players have apologized for uploading rogue applications which misuse the end consumer. They try hard to provide a safe environment for us. Still, we as customers should be aware of the threats associated with the malicious applications to protect ourselves.
A common threat associated with the disguised malicious app is spyware. It collects user information or behavior and sends it to the developers. Such data contain your banking passwords, account login details, credit card number, and more. Eventually, you might end up being a victim of blackmail, identity theft, or a financial scam.
2. Malvertising
Malvertising is a portmanteau or a blend of malware and advertising. It works by using an ad network to spread malicious applications on user devices.
This approach doesn’t look suspicious in the beginning. You will see these malicious ads as regular ones on websites or apps. However, cybercriminals have interfered with the ad network to insert their code.
The ad will download malware on your phone as you click it. Another vigorous technique uses a fullscreen ad to distract you. The ad appears as a pop-up on your screen. Eventually, people tend to touch their screens to close the ad. However, it will trigger malicious downloads on your phone.
3. Scams
Scams are one of the most common infiltrating techniques. It relies on the end-user to willingly open a link provided through either an email or text message. In some cases, a pop-up or link redirect can also work as a disguise for these websites.
Such links will lead you to malicious pages, which in turn download malware on your device. Else, the website will fetch sensitive information by asking you to fill a form. A few questions like your pet name, mother’s name, first school, and more appear as general information. However, many websites use them as your security questions. Therefore, giving up such information might tamper with your online security.
You have to be aware of the websites you are visiting. Always check if they are secure sites, especially if you make financial transactions or upload sensitive information.
Keep a habit of reading the website URL carefully. It will assure you about its legitimacy. Many scam sites appear similar to some popular websites like Amazon, PayPal, and more. At last, avoid clicking on malicious links knowingly.
4. Direct-to-device
It might be the most compelling way to load malware on your smartphone. You might recall this one from one of the crime movies.
The direct-to-device method requires the hacker to access the user’s device physically. Usually, criminals plug the device into a computer to install the malware. Otherwise, they can use a USB stick in some cases. This method is commonly known as sideloading as well.
As fascinating or fictitious it may sound, most high-profile attacks use this method. A specifically trained group of hackers target high-profile individuals and install malware on their phones when they leave it unattended.
Types of Smartphone Malware
Smartphone malware programs are rarer than desktop malware. Still, it does not nullify the threat they pose. As new users are adapting to the market, more robust smartphone threats are emerging daily.
Mobile malware can be categorized in multiple forms. However, it is worth mentioning that a particular malware can fall into one too many categories.
A particular category would only explain the main functionality of the malware. However, spyware can also be adware if it is showing you unnecessary pop-ups while stealing your data.
That said, here is the various type of malware programs for smartphones.
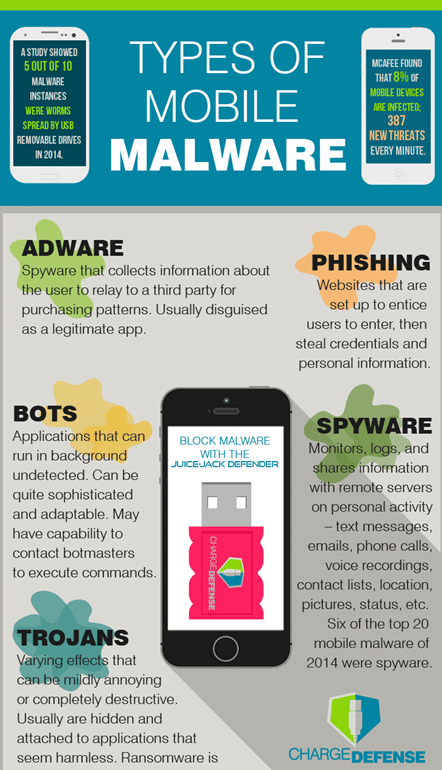
- Adware: It shows multiple ads to users on their home screen or notification panel. These ads often lead to malicious web pages or unintended redirects.
- Banker malware: It tries to steal your bank credentials without your knowledge.
- Ransomware: Locks the device or files on it and demands money in exchange for the decryption key.
- Rooting malware: Unlocks escalated permission on your device by rooting it.
- SMS malware: It intercepts your text messages and manipulates your phone to send encrypted messages. You might experience unnecessary mobile bills. There is also a chance of exposing OTP for logins and transactions.
- Spyware: it monitors your activity and app usage and sends the report to cybercriminals.
- Trojan: It appears as legitimate software and resides in your phone. However, it later opens the door for more malware programs to enter your device.
How to Remove Virus from Android Phone
There are multiple ways to detect ways on an Android phone than on an iPhone. You can use free apps readily available on the Play Store to scan your device for malware.
However, you won’t need that if you are sure about having a rogue app on your phone. You can remove one such app by going to Settings>Apps and select the app you want to uninstall.
Remember to clear cache and data before removing the application so it won’t leave aunty trace in your phone. Finally, select uninstall to remove the rogue application from your device.
To keep your phone secure from such threats in the future, you should consider installing an antimalware app as well. There are plenty of options available, out of which MalwareFox, Kaspersky, Avast, and Malwarebytes show promising results.
How to Stay Safe from Android Malware
No matter how hard you try, you can not stop cybercriminals from attempting to push a threat to your device. It can occur through multiple methods like sending a malicious message, tweaked app, pop-up, and more.
Therefore, you should focus on educating yourself to detect and stay away from such attempts. For instance, look at the website URL to confirm its legitimacy. Look for suspicious email addresses if the sender is unknown. Mainly, you should never leave your phone unattended in an unfamiliar environment.
A few more steps to better your security is installing an antimalware program. Besides, always avoid installing apps from unknown locations. It is essential if you are getting a paid app for free. Stay away!
Lastly, if you think you are compromised, remove the rogue application as soon as possible and change all your passwords if possible.